Some days back I had a discussion with an Azure SQL Database engineer about the need of rebuilding indexes on SQL Database. I thought that was a best practice but the engineer told me that the task was accomplished automatically as part of the managed service, in the same way you haven’t had to execute any file related task.
I remembered the thing today and found two interesting articles from Alexandre Brisebois just confirming my initial thoughts, that the indexing management is under your responsibility, and you need to pay attention to how fragmented they are.
There are three good blog posts from Alexandre on the matter I found interesting:
- Don’t forget about Index Maintenance on Windows Azure SQL Database
- Indexes are crucial on Windows Azure SQL Database
- Using PowerShell to Rebuild Azure SQL Database Indexes
Running the following T-SQL on a SQL Database, you can get the index fragmentation on a specific table in percent:
SELECT name, avg_fragmentation_in_percent
FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats (
DB_ID(N'MyDatabaseName')
, OBJECT_ID('MyTableName')
, NULL
, NULL
, NULL) AS a
JOIN sys.indexes AS b
ON a.object_id = b.object_id AND a.index_id = b.index_idIf you want to get all the indexes in a database with more than a 30% of fragmentation, you can run this other one:
SELECT name, avg_fragmentation_in_percent
FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats (
DB_ID(N'MyDatabaseName')
, NULL
, NULL
, NULL
, NULL) AS a
JOIN sys.indexes AS b
ON a.object_id = b.object_id AND a.index_id = b.index_id
WHERE avg_fragmentation_in_percent > 30
And now don’t be scared when seeing the results. The good news is that you are going to get better performance after rebuilding the indexes without having to scale to another SQL Database tier. Alexandre itself commented something about the possibility of using Azure Automation to do the task.
Reindexing using Azure Automation
I’m in love with Azure Automation and all the small things that can be automated to do our daily job easier, mostly based on running a small script on a schedule. Curiously there is a PowerShell Workflow Runbook on the Automation Gallery that allows to fully automate the SQL Database reindexing. Let’s see how to configure it step by step:
1) Provision an Automation Account if you don’t have any, by going to https://portal.azure.com and select New > Management > Automation Account
2) After creating the Automation Account, open the details and now click on Runbooks > Browse Gallery
3) Type on the search box the word “indexes” and the runbook “Indexes tables in an Azure database if they have a high fragmentation” appears:
4) Note that the author of the runbook is the SC Automation Product Team at Microsoft. Click on Import:
5) After importing the runbook, now let’s add the database credentials to the assets. Click on Assets > Credentials and then on “Add a credential…” button.
6) Set a Credential name (that will be used later on the runbook), the database user name and password:
7) Now click again on Runbooks and then select the “Update-SQLIndexRunbook” from the list, and click on the “Edit…” button. You will be able to see the PowerShell script that will be executed:
8) If you want to test the script, just click on the “Test Pane” button, and the test window opens. Introduce the required parameters and click on Start to execute the index rebuild. If any error occurs, the error is logged on the results window. Note that depending on the database and the other parameters, this can take a long time to complete:
9) Now go back to the editor, and click on the “Publish” button enable the runbook. If we click on “Start”, a window appears asking for the parameters. But as we want to schedule this task, we will click on the “Schedule” button instead:
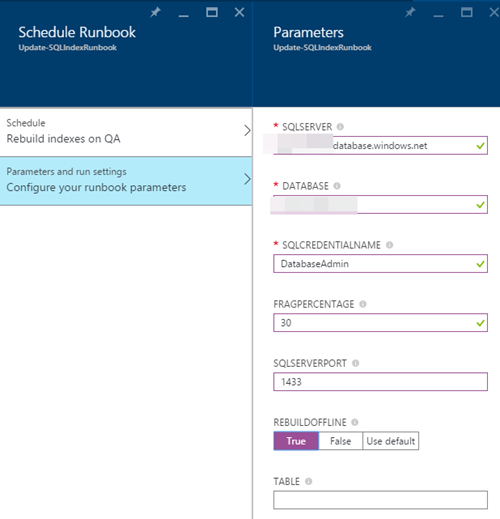
10) Click on the Schedule link to create a new Schedule for the runbook. I have specified once a week, but that will depend on your workload and how your indexes increase their fragmentation over time. You will need to tweak the schedule based on your needs and by executing the initial queries between executions:
11) Now introduce the parameters and run settings:
NOTE: you can play with having different schedules with different settings, i.e. having a specific schedule for a specific table.
With that, you have finished. Remember to change the Logging settings as desired:
Conclusion
Cool? SUPERCOOL!!
Un saludo y happy coding!